Acupuncture is one of the primary techniques used in the practice of Traditional Chinese Medicine. It is an option which is practiced globally as both a primary and adjunctive treatment of pain and some other symptoms for a wide range of health conditions.
Acupuncture retains a strong relevance in modern society and involves the placing of fine sterile needles in specific points of the body.
Many health practitioners may recommend acupuncture as an adjunct treatment that may assist with treatment. There is continuing research about how acupuncture can assist with treatments and you should consult your treating practitioner about how acupuncture may be able to help you.
Click here to view research references
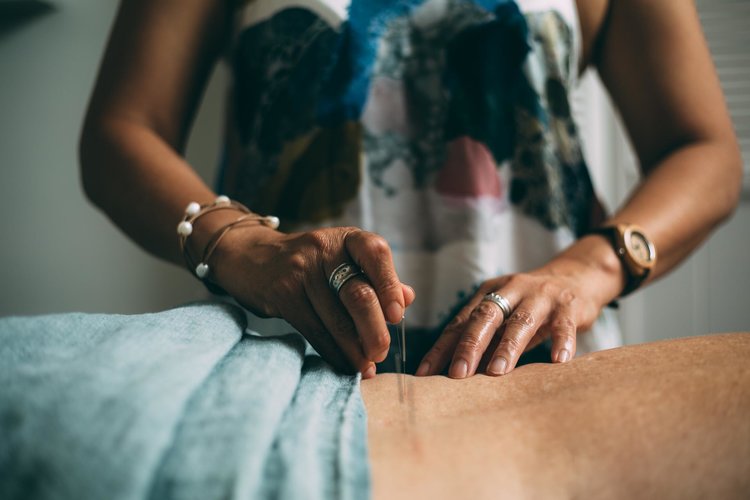
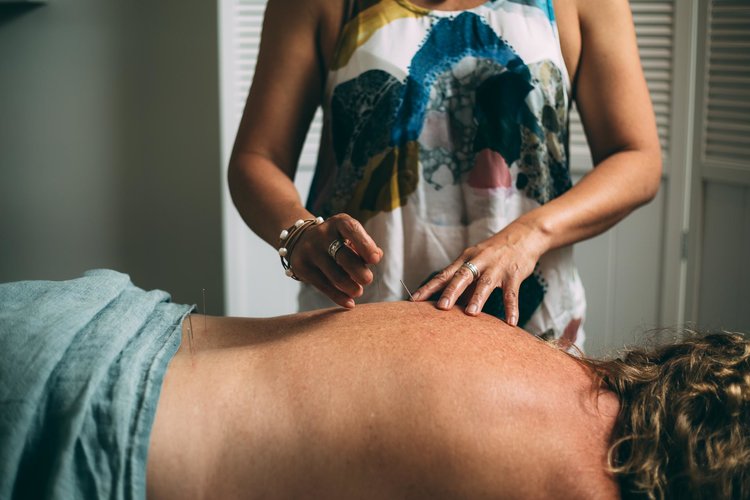

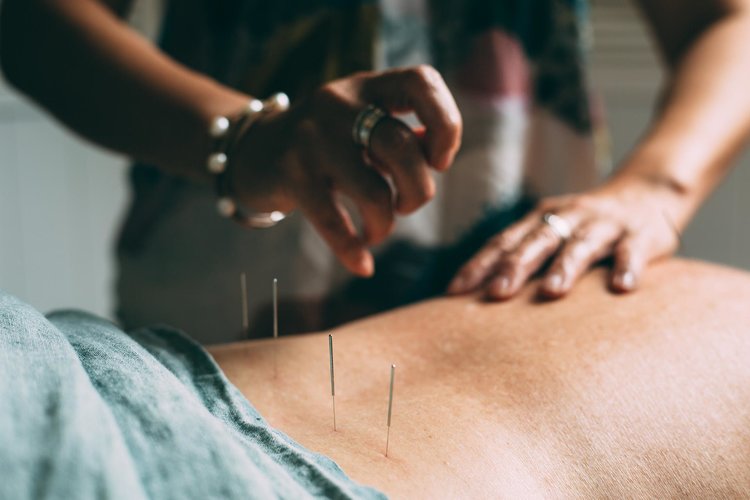
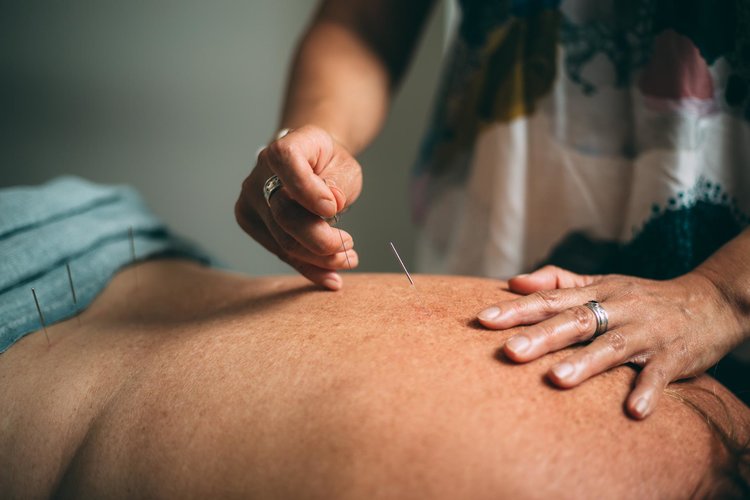

Cronulla Acupuncture and TCM – Pure Alchemy
Latest Blog Posts
 The Foods That Cause High Inflammation Diet plays a big role in inflammation, and many foods may cause inflammatory responses. Read more
The Foods That Cause High Inflammation Diet plays a big role in inflammation, and many foods may cause inflammatory responses. Read more Have You Heard Of Mugwort? Mugwort is more just reserved for the witches and wizards of Hogwarts, it has amazing healing benefits for even us… Read more
Have You Heard Of Mugwort? Mugwort is more just reserved for the witches and wizards of Hogwarts, it has amazing healing benefits for even us… Read more Tired? Your Qi (Ch’i) May Be Out of Balance Are you feeling tired all the time, sluggish, or in a low mood? It could be because your Qi is… Read more
Tired? Your Qi (Ch’i) May Be Out of Balance Are you feeling tired all the time, sluggish, or in a low mood? It could be because your Qi is… Read more
